5333486
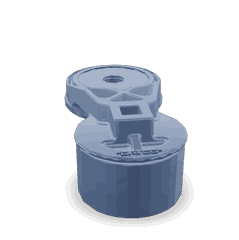
Belt Tensioner
Cummins®
IN STOCK

More than 10 are currently available
Ships within 1 business day
This truck part is made by Cummins®. We guarantee that all of our parts are from the OEM (original equipment manufacturer), ensuring a proper fit and quality manufacturing.
We honor the warranty provided by the original equipment manufacturer.
Introduction to Belt Tensioners
A belt tensioner is a critical component in the engine of a commercial truck, ensuring that the serpentine belt maintains the correct tension. This tension is essential for the efficient operation of various engine accessories, such as the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump. Without proper tension, these accessories can malfunction, leading to decreased performance and potential engine damage 1.
How a Belt Tensioner Works
The belt tensioner operates by applying a consistent force to the serpentine belt, keeping it taut. This is typically achieved through a spring-loaded mechanism or a hydraulic system. The tensioner adjusts to the wear and stretch of the belt over time, ensuring that the belt remains properly aligned and tensioned. This mechanism is essential for maintaining the balance and efficiency of the engine’s operation 2.
The Role of the Cummins 5333486 Belt Tensioner
The Cummins 5333486 belt tensioner is specifically designed for use in heavy-duty trucks, providing reliable and durable performance under demanding conditions. This part ensures that the serpentine belt maintains the correct tension, which is critical for the efficient operation of the engine’s accessories. By keeping the belt properly tensioned, the 5333486 belt tensioner helps to prevent slippage, reduce wear, and extend the life of the belt and related components 3.
Importance in Truck Operations
In the context of commercial truck operations, the proper functioning of the belt tensioner is paramount. The belt tensioner ensures that the engine’s accessories operate smoothly, which is essential for maintaining the overall performance and reliability of the truck. A malfunctioning belt tensioner can lead to a variety of issues, including belt failure, accessory malfunction, and potential engine damage. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the belt tensioner are critical to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the truck’s engine.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the belt tensioner are essential to prevent issues and ensure optimal performance. Here are some troubleshooting tips and maintenance practices:
-
Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the belt tensioner for signs of wear, such as cracks, corrosion, or damage to the spring or pivot points. Check the belt for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or glazing.
-
Tension Check: Ensure that the belt is properly tensioned. A loose or overly tight belt can indicate a problem with the belt tensioner. Use a tension gauge to measure the belt tension and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Lubricate Moving Parts: Ensure that all moving parts of the belt tensioner are properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Use a suitable lubricant recommended by the manufacturer.
-
Replace Worn Components: If any components of the belt tensioner are worn or damaged, replace them promptly to prevent further issues. This includes the spring, pivot points, and any other movable parts.
-
Check for Proper Alignment: Ensure that the belt is properly aligned with the pulleys. Misalignment can cause excessive wear on the belt and tensioner.
About Cummins
Cummins is a global power leader and a pioneer in the design and manufacture of engines, engine components, and related technologies. With a reputation for quality, reliability, and innovation, Cummins products are trusted by fleet operators and mechanics worldwide. The company’s commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction has made it a leader in the commercial truck and heavy-duty industry.
Expertise and Authority
As an expert in commercial truck parts, it is essential to understand the critical role that components like the Cummins 5333486 belt tensioner play in the overall performance and reliability of heavy-duty trucks. By providing detailed and comprehensive information, this article aims to educate engineers, mechanics, truck drivers, and fleet operators on the importance of proper belt tensioner maintenance and troubleshooting. With a focus on delivering valuable insights and practical advice, this content is designed to help readers achieve their objectives and maintain the efficiency of their commercial trucks.
Belt Tensioner Part 5333486 Compatibility with Cummins Engines
The Belt Tensioner part number 5333486, manufactured by Cummins, is designed to fit a variety of Cummins engines. This part is integral in maintaining the proper tension of the engine’s serpentine belt, ensuring efficient operation of ancillary components such as the alternator, water pump, and air conditioning compressor.
Compatible Engines
- 4B3.9
- 6B5.9
- B4.5
- B5.9 G
- F3.8 CM2620 F137B
- F4.5 CM2620 F139B
- ISB5.9G CM2180
- ISF3.8 CM2220 AN
- QSB7 CM2880 B117
Grouping of Compatible Engines
-
4B3.9, 6B5.9, B4.5, B5.9 G: These engines are typically found in smaller to medium-sized applications, often in agricultural and construction equipment. The Belt Tensioner part 5333486 is engineered to handle the specific load and operational conditions of these engines.
-
F3.8 CM2620 F137B, F4.5 CM2620 F139B: These engines are part of the Cummins F-Series, known for their reliability and performance in heavy-duty applications. The Belt Tensioner part 5333486 is designed to withstand the higher RPMs and greater stress associated with these engines.
-
ISB5.9G CM2180, ISF3.8 CM2220 AN: These engines are part of the Cummins ISB/ISF series, widely used in both on-highway and off-highway applications. The Belt Tensioner part 5333486 is tailored to fit these engines, ensuring optimal belt tension across various operational scenarios.
-
QSB7 CM2880 B117: This engine is part of the Cummins QSB series, known for its durability and efficiency in demanding industrial applications. The Belt Tensioner part 5333486 is compatible with this engine, providing the necessary tension to support the engine’s belt system.
Each of these engines benefits from the precise engineering of the Belt Tensioner part 5333486, ensuring that the serpentine belt operates at the correct tension, which is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of the engine’s ancillary systems.
Role of Part 5333486 Belt Tensioner in Engine Systems
The part 5333486 Belt Tensioner is integral to maintaining the proper function and efficiency of various engine components through its interaction with the drive belt system.
When the engine is operational, the Belt Tensioner ensures that the drive belt remains taut. This tension is essential for the efficient transfer of power from the engine to components such as the alternator and other auxiliary systems.
The alternator drive relies on consistent belt tension to spin the alternator rotor, which in turn generates electricity to power the vehicle’s electrical systems and recharge the battery. Without adequate tension, the alternator may not operate efficiently, leading to potential electrical issues.
Additionally, the Belt Tensioner plays a role in the overall durability and longevity of the drive belt. By maintaining the correct tension, it prevents the belt from slipping or becoming overly tight, which can cause premature wear and potential failure of the belt or connected components.
In summary, the part 5333486 Belt Tensioner is a key component in ensuring that the drive belt system operates smoothly, thereby supporting the efficient function of the alternator and other engine-driven accessories.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical role of the Cummins 5333486 Belt Tensioner in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of heavy-duty truck engines is essential for engineers, mechanics, and fleet operators. Regular maintenance, proper troubleshooting, and timely replacement of this part are crucial to ensuring the longevity and performance of the truck’s engine. By adhering to these practices, operators can avoid potential issues and maintain the optimal operation of their vehicles.
SPECIFICATIONS
RECOMMENDED PARTS
* Variable geometry turbocharger and electronic actuator repairs are not eligible to be claimed as over-the-counter under New or ReCon parts warranty for parts installed after October 1, 2018.
* Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC), Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF), Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) catalyst, and Electronic Control Module (ECM) repairs are not eligible to be claimed as over-the-counter under New or ReCon parts warranty for parts installed after January 1, 2020.
* These restrictions are only applicable to New parts and ReCon parts coverages for the components listed above sold to a customer in the US or Canada. All other coverages are excluded. All other regions are excluded.